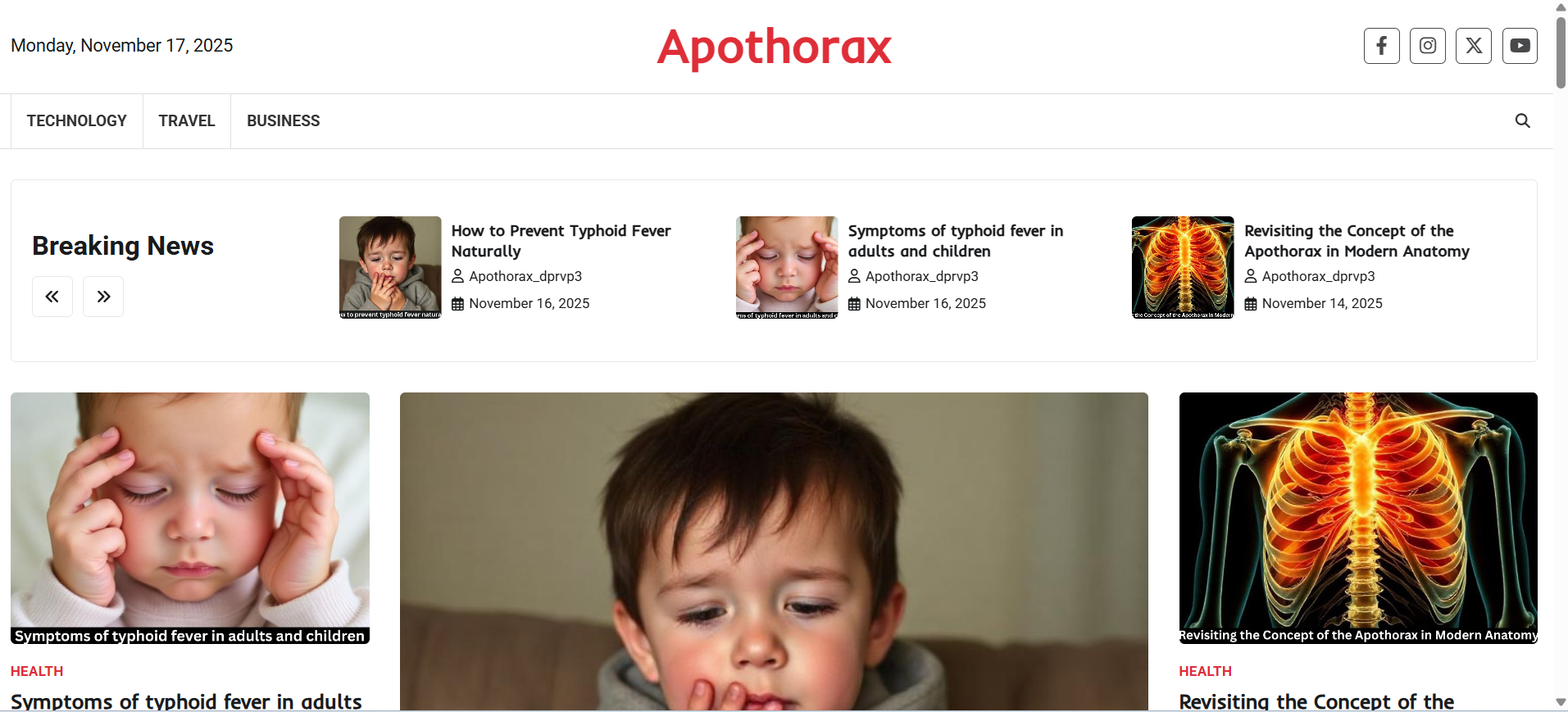
Modern anatomy is filled with standardized, precise terminology—but every so often, you come across an older term like apothorax, and it leaves you wondering: Does this concept still matter? Surprisingly, yes. Even though the apothorax isn’t widely mentioned in modern textbooks, understanding it provides useful insights into thoracic structure and function.
Why Study Outdated Anatomical Terms?
Because many of them help explain transitional or supportive regions of the body—areas that don’t fit neatly into modern classifications.
Importance of the Apothorax in Structural Understanding
The term highlights how the body supports and protects the thoracic cavity, offering context that enhances your anatomical knowledge.
What Is the Apothorax?
Simple Definition
The apothorax refers to the supportive region around the thorax, primarily located along the lower sides of the chest wall.
Etymology and Origin
“Apo” means “around or supporting,” while “thorax” refers to the chest. Together, the term describes the region supporting the thoracic cavity.
Why the Term Isn’t Common Today
Modern anatomy prefers more precise terminology, focusing on individual muscles, bones, and tissues rather than broad descriptive regions.
Location of the Apothorax
Anatomical Placement
You’ll find the apothorax:
- Along the lateral lower chest
- Near the diaphragm’s upper boundary
- Surrounding the lower ribs
Boundaries and Connecting Regions
Although unofficial, it typically includes:
- Ribs 8 through 12
- Costal cartilages
- Intercostal spaces
- Upper abdominal structures
Relationship With the Thoracic Cavity
The apothorax forms a supportive transition zone between the thoracic cavity above and the abdominal cavity below.
Structures Making Up the Apothorax
Muscles
Key muscles in this region include:
- External and internal intercostals
- Innermost intercostals
- Serratus anterior
- External oblique
- Upper transversus thoracis
These muscles are crucial for breathing and trunk movement.
Bones and Cartilage
The area contains:
- Lower ribs
- Costal cartilages
- Portions of thoracic vertebrae
Nerves, Blood Vessels & Connective Tissue
Key components include:
- Intercostal nerves
- Thoracic spinal nerves
- Intercostal vessels
- Connective tissues and lymph structures
Functional Importance of the Apothorax
Support for Breathing
The apothorax plays a vital role in helping the ribs expand and contract with each breath.
Stabilizing the Chest Wall
It provides foundational support to maintain rib cage structure and protect internal organs.
Protecting the Thoracic Organs
By reinforcing the chest wall, it helps shield the heart, lungs, and major vessels from injury.
The Apothorax in Movement & Posture
Role in Core Stability
Muscles in this region contribute significantly to core strength.
Role in Trunk Flexion & Rotation
Every time you twist your torso or bend sideways, the apothorax’s structures are involved.
Importance in Daily Mechanics
This region helps with:
- Lifting
- Bending
- Breathing
- Maintaining balance
Apothorax vs. Thorax
Structural Differences
- Thorax: a defined cavity containing vital organs
- Apothorax: the area around the thorax supporting external structure
Functional Differences
- Thorax: handles breathing and circulation
- Apothorax: supports chest movement and stability
Why Students Confuse the Two
Because the names are similar—but one is a cavity, and the other is an external region.
Clinical Relevance of the Apothorax
Injuries Affecting the Region
Rib fractures and muscle strains are common in this area.
Respiratory Disorders Linked to Thoracic Support
Weakness in the apothorax can affect breathing efficiency.
Importance in Diagnosing Chest Wall Pain
Many chest wall pain syndromes originate from this supportive region.
Why the Apothorax Still Matters in Modern Anatomy
Value in Anatomical Education
It helps students understand how thoracic structures interconnect.
Understanding Transitional Body Regions
The apothorax bridges the thoracic and abdominal systems.
Importance in Comparative Anatomy
The concept is still relevant when studying animals with varied thoracic designs.
Learning the Apothorax: Tips & Techniques
Mnemonics
Try this simple one:
“Apo supports the thorax.”
Diagram-Based Visualization
Use anatomy charts or 3D models to locate the region accurately.
How to Connect It to Modern Anatomy Terms
Study it alongside:
- Ribs
- Intercostal muscles
- Diaphragm
- Thoracic wall structures
Conclusion
The apothorax may not be a dominant term in modern anatomy, but it remains an important concept for understanding the thoracic support system. By revisiting this idea, students gain a clearer view of how the ribs, muscles, and connective tissues work together to protect vital organs and maintain posture. Whether you’re preparing for exams or expanding your anatomical knowledge, understanding the apothorax adds valuable depth to your learning.
FAQs
1. Is the apothorax still used in modern anatomy?
It’s rarely used today but still helpful for understanding thoracic support.
2. Does the apothorax contain organs?
No, it contains supportive structures around the thorax.
3. What is the main function of the apothorax?
To support breathing, stabilize the chest wall, and protect internal organs.
4. Why study outdated anatomical terms?
Because they help explain transitional regions that modern terms often simplify.
5. Is the apothorax important in clinical diagnosis?
Yes, especially for chest wall injuries, muscle strains, and pain syndromes.